概述
相似点:
通知目标类某一个事件发生,目标类接受到通知后做出相应处理。
不同点:
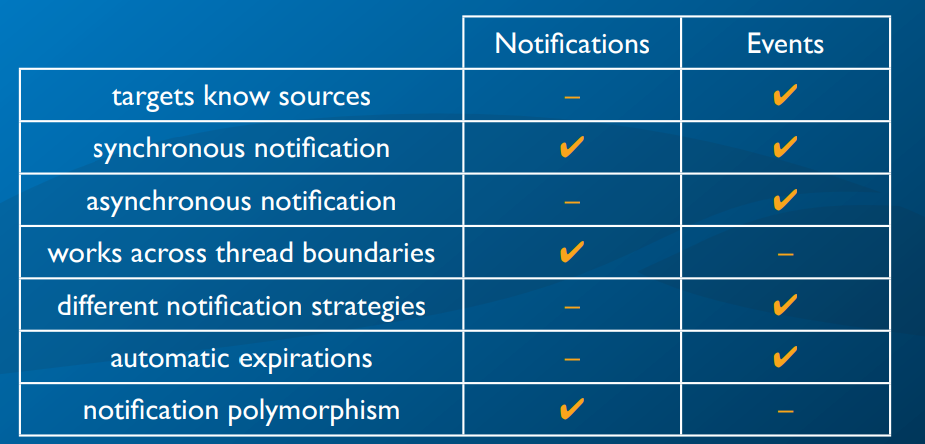
- Notifications 被应用于观察者不关心通知来源的场景。Events 被应用于观察者需要知道通知来源,或者只接受特定来源通知的场景。
- Notifications 只支持同步通知,Events 同时支持同步和异步通知。
- Notifications 可以跨线程工作,但是 Events 不行。
- Events 可以有多种通知策略,Notifications 不支持。
- Notifications 支持消息继承,Events 不支持。
Notifications
Notification Class
Poco支持自定义消息类,只需要继承于 Poco::Notification 类就可以当做消息来使用,并且可以被Poco的智能指针包裹。一个消息类可以携带任意数量的数据和包含任意操作。注意,Notification 类不具有值语义特性(一个对象被系统标准的复制方式复制后,与被复制的对象之间毫无关系,可以彼此独立改变互不影响),并且通常被创建于堆上。
NotificationCenter Class
Poco::NotificationCenter 负责调度消息对象,其使用 observer 对象(基类为Poco::AbstractObserver) 来告知消息传达的目标。一个 observer 对象储存着一个指向目标的指针和一个指向目标回调成员函数的指针。
目标可以通过向 NotificationCenter 注册来接收消息,也可以删除注册不再接收消息:
void addObserver(const AbstractObserver& observer)
//registers a notification target with the NotificationCenter
void removeObserver(const AbstractObserver& observer)
//unregisters a notification target
Observers
Observers 分为 Observer 和 NObserver 两类模板,Observer 应用于 Notification 对象的裸指针,而 NObserver 则应用于 AutoPtr<Notification> 。
对于 Observer 来说,目标函数声明必须形似:
void someCallback(SomeNotification* pNf)
对于 NObserver 来说,目标函数声明必须形似:
void someCallback(const AutoPtr<SomeNotification>& pNf)
发送消息
NotificationCenter 使用 postNotification() 成员函数发送消息。
void postNotification(Notification::Ptr pNotification)
例子:
#include "Poco/NotificationCenter.h"
#include "Poco/Notification.h"
#include "Poco/Observer.h"
#include "Poco/NObserver.h"
#include "Poco/AutoPtr.h"
#include <iostream>
using Poco::NotificationCenter;
using Poco::Notification;
using Poco::Observer;
using Poco::NObserver;
using Poco::AutoPtr;
//支持继承的消息类
class BaseNotification: public Notification
{
};
class SubNotification: public BaseNotification
{
};
class Target
{
public:
//BaseNotification的回调函数
void handleBase(BaseNotification* pNf)
{
std::cout << "handleBase: " << pNf->name() << std::endl;
pNf->release(); // we got ownership, so we must release
}
//SubNotification的回调函数
void handleSub(const AutoPtr<SubNotification>& pNf)
{
std::cout << "handleSub: " << pNf->name() << std::endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
NotificationCenter nc;
Target target;
//注册Observer
nc.addObserver(
Observer<Target, BaseNotification>(target, &Target::handleBase)
);
//注册NObserver
nc.addObserver(
NObserver<Target, SubNotification>(target, &Target::handleSub)
);
//发送消息
nc.postNotification(new BaseNotification);
nc.postNotification(new SubNotification);
//取消注册
nc.removeObserver(
Observer<Target, BaseNotification>(target, &Target::handleBase)
);
nc.removeObserver(
NObserver<Target, SubNotification>(target, &Target::handleSub)
);
return 0;
}
NotificationQueue
NotificationQueue 可以跨线程传递消息。多个线程可以同时从 NotificationQueue 读消息。NotificationQueue 的作用一般有:
- 后台处理线程给UI线程传递消息。(解耦合)
- 从控制线程给一个或多个工作线程传递消息。
获取消息队列里的消息一共有以下几种方法:
void enqueueNotification(Notification::Ptr pNotification)
//enqueues the given notification by adding it to the end of thequeue (FIFO principle). The queue takes ownership of the notification.
void enqueueUrgentNotification(Notification::Ptr pNotification)
//enqueues the given notification by adding it to the beginning of the queue (LIFO principle). The queue takes ownership of the notification.
Notification* dequeueNotification()
//dequeues the next pending notification from the beginning of the queue, or null if no notification is available. The caller gains ownership of the notification.
Notification* waitDequeueNotification()
Notification* waitDequeueNotification(long timeout)
//dequeues the next pending notification. If no notification is available, waits (at most timeout milliseconds) for a notification to be posted. Returns the notification, or null if none is available.
关闭消息队列的方法:
- 发送特殊的消息 QuitNotification 给其他线程。
- 设置一个全局的终止信号并且向 waitDequeueNotification() 中添加等待时长参数。
- 使用NotificationQueue成员函数 wakeUpAll() 。每一个被调用的 waitDequeueNotification() 会立即返回。 wakeUpAll() 只在工作线程处于等待消息时才起作用。
特殊的队列:
- PriorityNotificationQueue:消息标注优先级,在队列中按照优先级来排序。
- TimedNotificationQueue:消息标注时间戳,在队列中按照时间顺序来排序。
Events
Poco的Events是模仿C#的events而来的,但是是用纯C++的方式实现的。相比Notification,Event只是实现类的一部分,通常被定义为类中的一个公有成员。Events支持异步通知。
Event 用于发送通知,均继承于 Poco::BasicEvent 。一个Event可以携带一个继承于Poco::EventArgs 的参数。目标接收通知时需要使用到 Poco::Delegate 类。
#include "Poco/BasicEvent.h"
#include "Poco/Delegate.h"
#include <iostream>
using Poco::BasicEvent;
using Poco::Delegate;
class Source
{
public:
BasicEvent<int> theEvent; //公有成员,int类型参数
void fireEvent(int n)
{
theEvent(this, n); //发送通知,同步
// theEvent.notify(this, n); //另一种写法,同步
// theEvent.notifyAsync(this, n); //异发送通知,异步
}
};
class Target
{
public:
//回调函数,格式:
//void handler(const void* pSender, EventArg& arg)
void onEvent(const void* pSender, int& arg)
{
std::cout << "onEvent: " << arg << std::endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Source source;
Target target;
source.theEvent += Poco::delegate(&target, &Target::onEvent); //注册委托
source.fireEvent(42);
source.theEvent -= Poco::delegate(&target, &Target::onEvent); //注销委托
return 0;
}
注意事项:
- 不要忘记注销委托。
- 一个Event可以注册两个委托,但是后面注册的委托会取代之前的委托。
- 注销从未注册过或者已注销的委托不会出错。
- Event是线程安全的。
特殊的Event:
- Poco::FIFOEvent :按通知到达的顺序去触发委托。
- Poco::PriorityEvent :按优先级去触发委托。必须使用 Poco::PriorityDelegate 才能生效。